We all know the basics of how Google works: you type in a search term and results are returned based on your search query. But do you really understand what each type of search result does, or how they work?
Organic search and paid search are only scratching the surface of the many types of search results that you may find. You’ll find video results, video carousels, top stories carousels, local results, and many others. Each type of result provides distinct information based on your search query. You don’t have to constantly refine your search in order to obtain different types of search results.
That’s the beauty of Google’s search results: in general, they tend to be easy to use and navigate to. The visual separation and highlighting of specific types of search results allow for easier access to the information you may need as a user. As an SEO, they give you more opportunities to target certain types of information along with certain types of queries.
In this guide, we take a closer look at the different types of search results on SERPs (search engine result pages) so that you can make better use of them when it comes to SEO.
Organic Search Results
What, exactly, are organic results? Well, they are the results that appear at the top of a SERP. They’re also called “natural” or “normal,” and you might see them referred to as regular search listings—or simply sitelinks.
How do organic rankings work? Google grades its pages according to quality and relevance in order to rank them accordingly in their natural search engine result page (SERP).
Organic results are all about the content on your site and how well it ranks for certain keywords or phrases related to what users have searched for earlier on Google’s search engine. The higher ranking position indicates better quality content and a better overall website quality. It’s also about links. Can you get rankings without links? Sure. But you’d better make sure your content is of the highest quality, delivers exceptional value to the user and doesn’t contain a ton of useless fluff.
Organic rankings work by utilizing many different algorithms under the hood, with the ultimate goal of higher quality content outranking lower quality content.
At least, that’s the idea. Does it always work? Not always. Sometimes, Google’s algorithms do not work for your site the way they should. Also, there may be other sites ranking higher than you that have been in place longer or even ones that rank the same as you but get more traffic because they’ve had more time on page and links from other sources pointing at their content.
This is where SERP features come into play. They’re either organic results or paid ads based on relevance to what users searched for earlier on their respective engines. SERP features help us break down different types of search results one might encounter when searching online!
This is an example of organic search results:
Pay Per Click Ads (PPC) Results
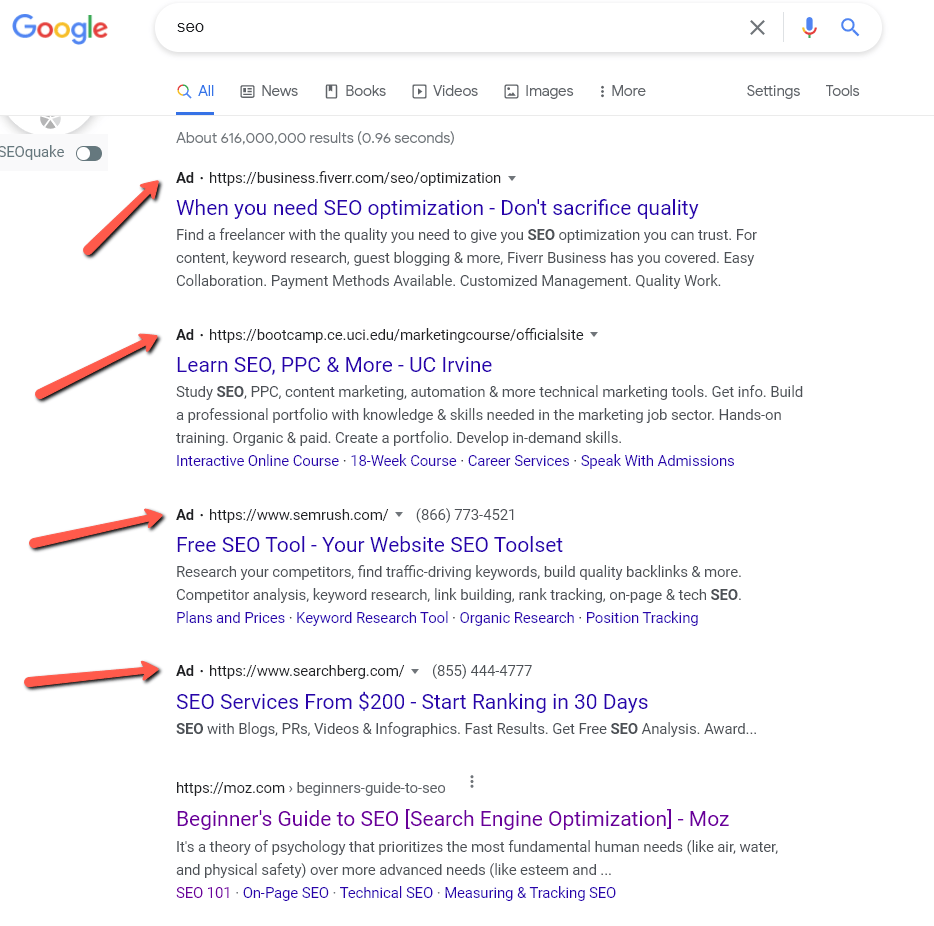
Paid ads are those results at the top of your search results that you may think you have to click on. You may see a text ad, image ad or video ad for these paid-for listings. The company pays Google per click. But it is important to mention this fact: paid ads do NOT help your organic ranking on Google. The two are completely different beasts and entirely unrelated from each other. Don’t believe the naysayers who try to tell you that the only way to get Google rankings is to pay for ads. They don’t know what they are talking about.
Paid ads work best when paired with organic (free) listing because using both maximizes visibility as well as traffic potential from both free and paid sources. It never hurts to be at the top of the first page even if there are other companies paying more than you. People use different criteria to choose which result they want after clicking on an organic link anyway, so just being higher up is better than a lower position, all things considered!
This is where a two-pronged strategy really shines. By identifying ways that you can maximize your search opportunities through both organic search and PPC, you can set a solid foundation with which to grow your organic and paid traffic.
Yet another example of this type of result is below, when you search for the query “4k gaming monitors.”
Ads also show up as “organic results” on Google, which puts further confusion on the reader, but at the very least Google does mark them as ads, as shown above. While Google does mark them as ads, less savvy computer users may not understand they are paid ads.
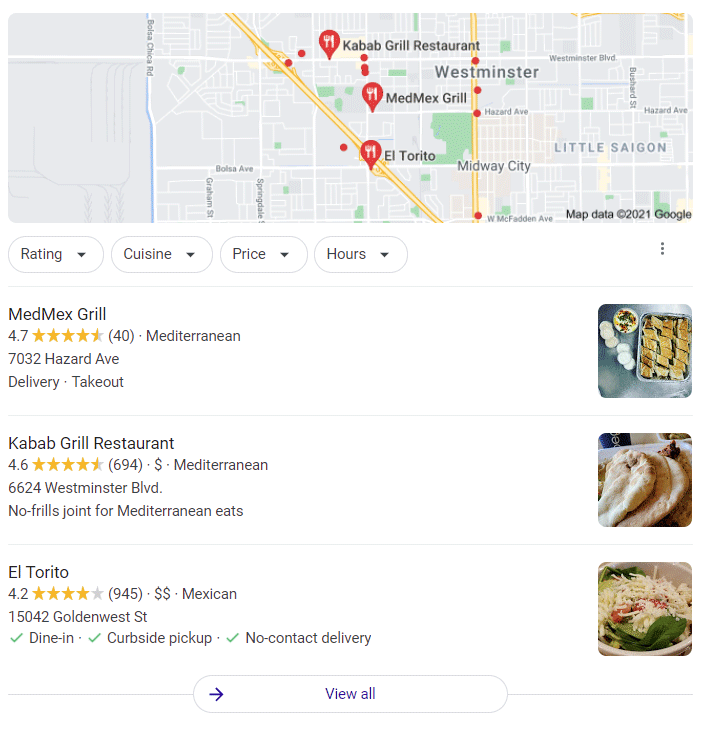
Local Packs
The local pack results are the three most relevant local results for a search, including map and business listings. If you click on “see more” next to one of them, it will expand to show all six in order from closest (the first) to furthest away.
Local packs are also where Google shows new place pages that it has collected if the user searched using an address or incorporated a location into their query like so: “best restaurants near me.” This can be helpful when they don’t have time or motivation to research every listing before clicking on any of them. But keep in mind that Yelp likely still provides better reviews than these aggregate sites do because its users are actively posting reviews as they visit their places of interest.
Featured Snippets
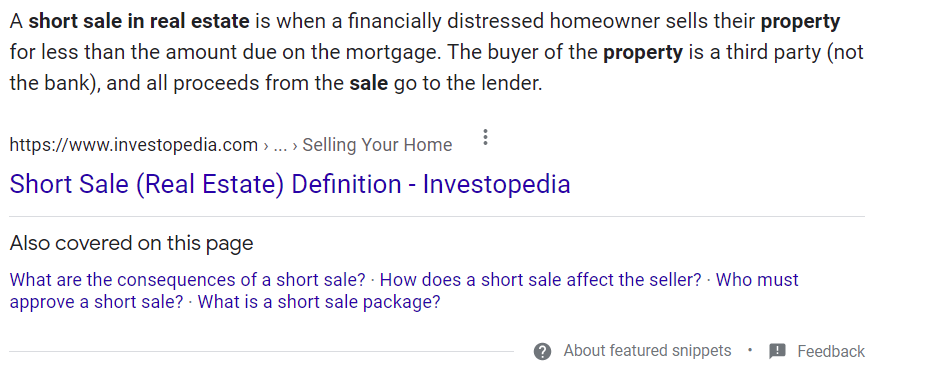
The Featured Snippet: this is a summary at the top of your search results that Google determines most relevant to your query. If you have the best quality, uniqueness, authoritativeness, relevance, and trust in terms of the entities you are optimizing for, you may end up winning the coveted featured snippet. This is also known as position zero.
This is better than position 1, as it usually places you above all the paid aids and Google organic results, which means that your site gets top tier exposure and traffic from that query.
This is one example of what a Featured Snippet looks like. The following featured snippet is for the query “what is a short sale in real estate.”
Top Stories
What are the top stories results? These results are based on a variety of factors, such as relevance to the query and freshness. These results will change throughout the day depending on what is happening in the world.
In its earliest version, Google’s top stories was actually a “News for” box.
Currently, they are a set of thumbnails.
The top stories box can change its appearance depending on the query, so there is no guarantee you will get top stories carousels that look the same from query to query.
For example:
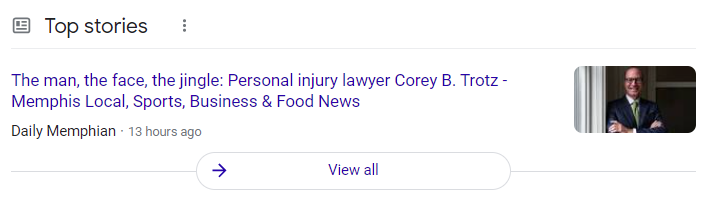
The top stories box looks like this for the query personal injury lawyers:
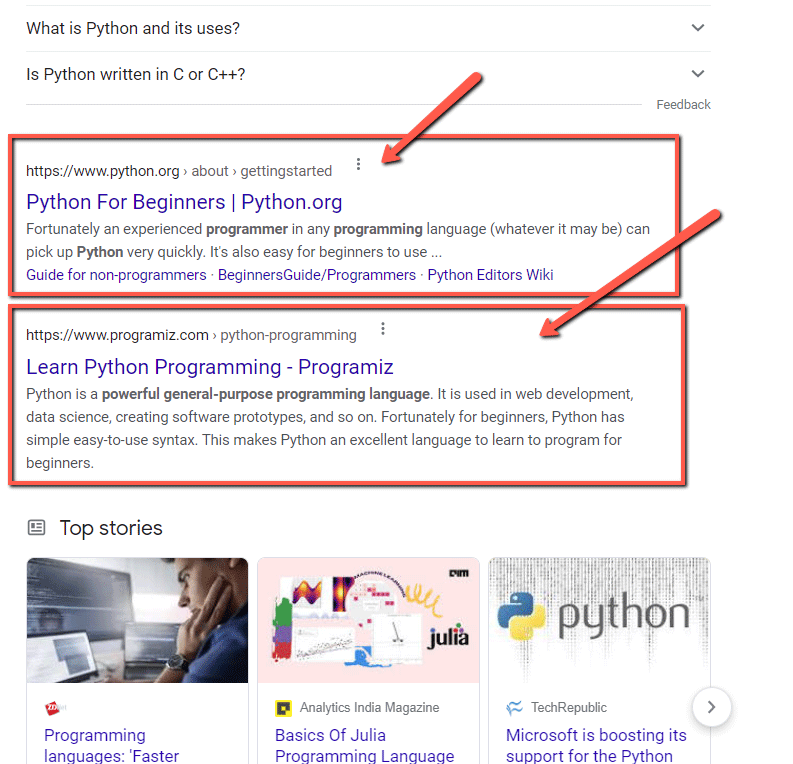
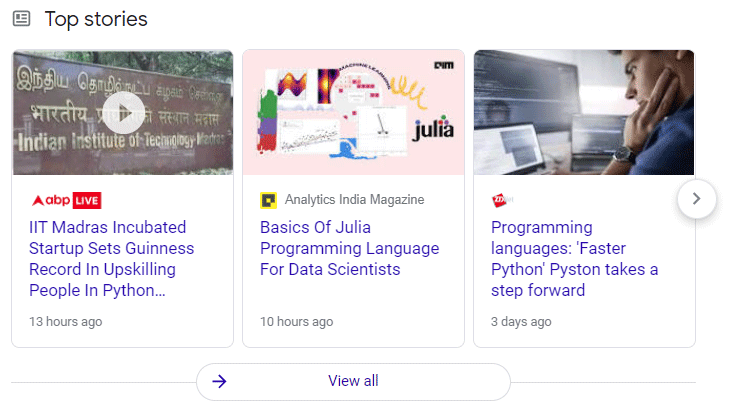
These are the top stories results for the query “python programming”:
These types of results display headlines and an excerpt from different news sources that have the most recent updates on those topics. The thumbnail size is usually within 150-200px in width and can be wider when it displays photos or videos. It also has two tabs for quick navigation between images (or videos) with headlines below them and text content accompanying the headline as well as related articles at the bottom half of those boxes.
Note that these may not always appear if Google determines there has been no new information published about a topic in the 24 hours since the last search was conducted.
The top stories section shows links to news articles that are currently popular around the world at this moment in time
It also includes a link to their most widely shared article for the day (which changes every hour).
In December 2016, Google replaced In the News with Top Stories. It was likely a change that was a long time coming due to the fake news scandal that hit at the time.
Note that Google’s Top Stories are not necessarily the top stories of today, or even this week. It changes every hour so it may be up to date at some point in time and then irrelevant later on.
The best way to optimize for Top Stories—while still trying to comprehend how all of these different SERP features work—is not to forget about traditional SEO practices like creating quality content, keeping your titles short, making sure that Google Search can find your story, using metadata, making sure page speed is fast enough and mobile friendly, including structured data, optimizing social media likes and shares and using relevant backlinks. Google’s Developer documentation has more information about optimizing your page for Top Stories.
Then, you can focus on some of the other SERP features that may be more specific to today’s news cycle.
Image Carousel
In the image carousel results, Google displays a series of images in different sizes. Clicking on any image will open up the full-size version within Google Images, but not clicking an enlarged image does not take you to another page.
The Image Carousel is primarily used for photography and aesthetic purposes, where it becomes more important that users can see what they are looking at without having to click through multiple pages.
It’s also helpful when there are so many results with similar text or titles that it may be difficult to choose between which ones to examine further (e.g., “Gucci Scarf” search). This feature allows people who want just the right photo (or don’t have time) to quickly find one by scanning through a set of photos fairly quickly.
This is one example of the image carousel showing up for the query “volcanoes in italy”:
Google Travel Results
Google’s travel results are these results that are focused on travel-related queries. The result will be a combination of destination information, images and weather.
Google search: flights to Rome
Result: Nearby airports (with flight prices), hotels in the area, sights nearby, attractions near the hotel
Example query: “luxury resorts”
Result: Lists top ten luxury resorts around the world with detail about each resort including cost range for per-night stay.
These types of results are critical to achieving some of the best deals on travel you can find nowadays.
By keeping the travel results on their platform, Google essentially becomes your own “travel search engine”.
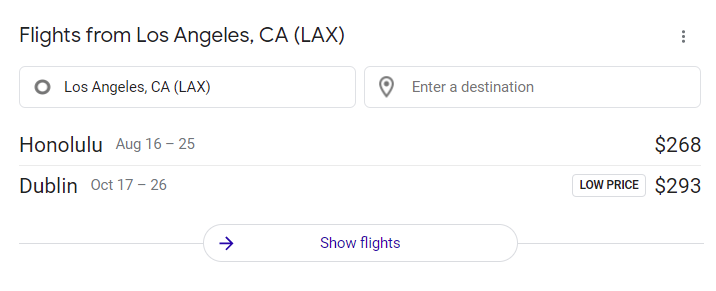
Here is an example of the travel results for the query “flights.” This type of search result is highly localized, so it will vary depending on your IP address and location.
Here is yet another example of travel results. This time, for the query “hotels in las vegas”:
Rich Snippets
When you think of rich snippets, you may think of the yellow star ratings in Google’s organic SERPs and not much more. But rich snippets can be so much more than just a quick glance at the stars. Let’s break down what they are:
- Organic listings with enhanced content;
- Knowledge panels that give users information about an entity or person;
- Image Carousels that displays images across various categories (images must be publicly available); and
- Featured Snippets with even richer information such as reviews from trusted sources like Yelp or TripAdvisor. These will change depending on your query.
If you want to get higher rankings for your business listing, it is important to have all of these features associated with it.
How Do You Optimize for Rich Snippets?
For an organic listing, you want to have all the necessary information: title, address and phone number (NAP), hours of operation, and website link. Depending on your type of business, you may not need to include all potential pieces of information. But, enough information to identify your business as the correct entity is recommended.
You may want to include your business name as well as your contact info, specifically your web address and email address in addition to NAP (your name, address, and phone number). This is also good for other businesses like doctors or lawyers but requires some specific knowledge about that industry as well.
Also, don’t forget Schema.org markup. This is the language used by Google to understand and organize specific data included on your pages, and they can generate a knowledge panel or enhanced business listing. Schema.org markup can be added to your site’s code either manually or automatically through a plugin like Yoast SEO or Rank Math (Rank Math is our personal favorite).
A Featured Snippet, depending on the query and snippet type, may include at least one photo, video, content snippet (usually from reviews), which should all link back to your website.
For Featured Snippets, it can be difficult because they change depending on searcher activity. In general though, there should be a description of your product or service with keywords included throughout so Google knows exactly what known entities to associate with your business.
The key piece of knowledge, if you learn nothing else from this post: make sure that Schema.org markup is present on any page that you want to rank in featured or rich snippets.
Knowledge Graph
Any discussion about the Google search results would be incomplete without talking about their knowledge graph – the method behind the madness of query and result organization.
The Google knowledge graph compiles information about topics and organizes them according to known entities. So long as Google knows all about these things, they are compiled in the knowledge graph as known entities. It’s a more efficient method of compiling and organizing information so it can easily be found by you, the user.
The knowledge graph is not limited to certain types of results, however. Google explains the knowledge graph as the following:
“Take a query like [taj mahal]. For more than four decades, search has essentially been about matching keywords to queries. To a search engine the words [taj mahal] have been just that—two words.But we all know that [taj mahal] has a much richer meaning. You might think of one of the world’s most beautiful monuments, or a Grammy Award-winning musician, or possibly even a casino in Atlantic City, NJ. Or, depending on when you last ate, the nearest Indian restaurant. It’s why we’ve been working on an intelligent model—in geek-speak, a “graph”—that understands real-world entities and their relationships to one another: things, not strings.
The Knowledge Graph enables you to search for things, people or places that Google knows about—landmarks, celebrities, cities, sports teams, buildings, geographical features, movies, celestial objects, works of art and more—and instantly get information that’s relevant to your query. This is a critical first step towards building the next generation of search, which taps into the collective intelligence of the web and understands the world a bit more like people do.”
Knowledge Panel
Knowledge Panel: This type of result appears next to the SERPs, and expands when clicked upon—it will typically consist of a summary box at the top and then multiple panels below relating to various known entities that Google understands about that search result.
Here is a screenshot of your typical knowledge panel:
Google Images
Google image search is the best way to find images on Google. Looking for something unique? You may want to make sure that you create your own (and be careful about copyright issues!)
The usual process involves typing one’s desired keyword(s) into the first field labeled “Images” at google.com. Google will then present a list of possible variations; each with their own thumbnail preview. Clicking on individual result thumbnails will allow you to flip through your choices in a photo-like manner, with the option to either view more images or search for something else.
This tool is quite powerful and provides both businesses as well as individuals many options. There are so many different types of information that can be found quickly by using this service!
Below is an example of what image search looks like:
Google Images also includes photo editing tools which enable people to add things like borders, captions or even change colors before publishing them on blogs or websites. The process involves loading photos into two fields: one where you type what content will appear on the left side of each image (such as “Borders”) and then another field where you input desired text (“Olympic Gold Medalist”).
Image Search API: In order to use the image search API, you will need a developer key. This API is useful for retrieving image metadata, downloading individual images or downloading all the photos from one particular search query. This can make searching for and curating images much easier than it otherwise would be through a manual process.
Google Travel
The Google Travel feature provides rankings on destinations by taking into account a number of variables. For example, the country’s GDP per capita and other economic factors are taken into consideration when determining hotel prices in Google search results.
Using Google Travel, you can save money by choosing the cheapest country and city for your desired destination.
Google also provides a selection of “expert-curated” hotels that includes various amenities such as business centers, fitness facilities, and private pools.
This page is great to find destinations you might not have considered before!
Tourists may want to use Google’s hotel search function in order to get more information about their accommodations at a given location without having to visit an external site or browse through different pages on the company website. This will save them time if they are trying out several places during their travels.
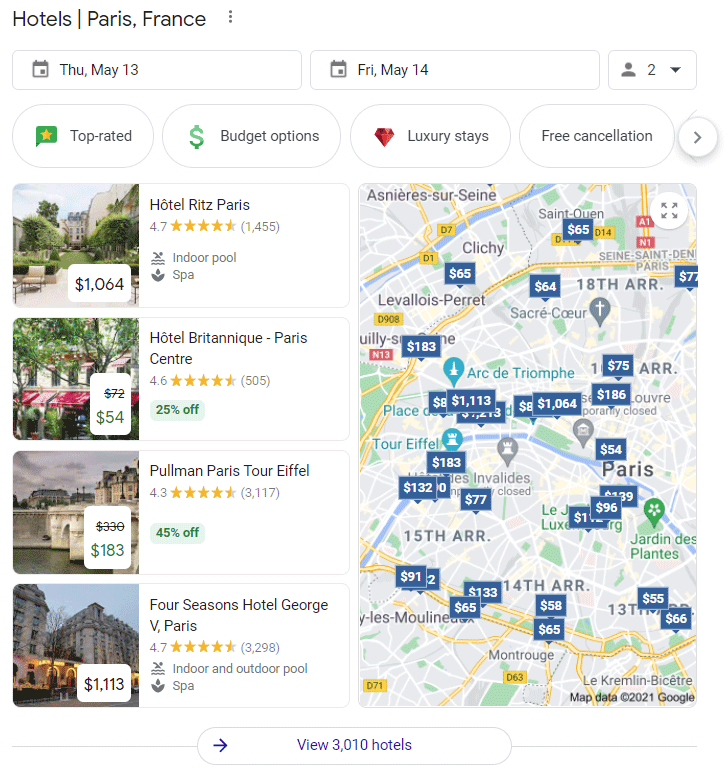
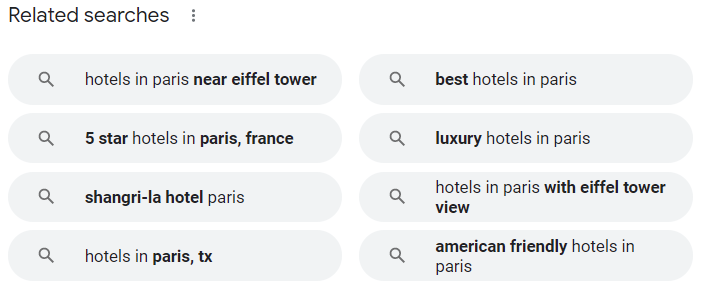
Revisiting our hotel example, here’s a demonstration of the hotel rich snippet. This time, for hotels in Paris, France.
People Also Ask
The people also ask answer boxes are related to one another semantically.
When a person clicks on the first autocomplete answer box, they will see more of these answer boxes that are all related in some way.
They may be people who have asked similar questions and recorded their question with an audio or video clip (similar to how webmasters can upload videos as responses).
Or they could simply provide additional information about what is being discussed in the main search result like recent news articles or current events which give context for why you searched this exact topic.
People also ask results are shown at the bottom right corner of any page when there is room available for them after other features such as ads, tabs/drawers, sitelinks etc., but if there isn’t enough space they’re not shown.
Here, people can ask questions that the search engine pretends to be answered by other users and provide relevant answers.
The answers are often formatted in a question/answer format where most of the answer is provided as a link for more information.
Here’s an example of the people also ask results:
Related searches also show up alongside people who also asked this same question at the bottom of any page when there’s room available after ads etc., but if there isn’t enough space, it doesn’t appear on your screen. There might only be two related search results or four depending on your query, and depending on what people have asked.
In the example below, there are eight related searches results.
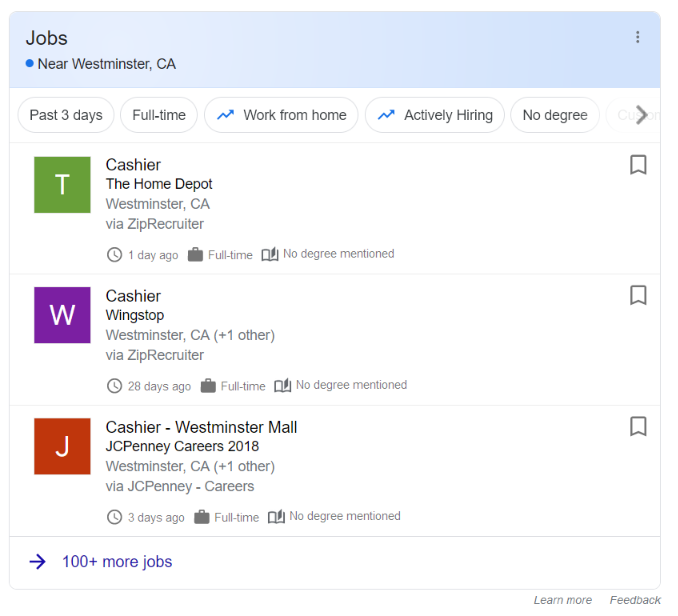
Jobs Pack
The Google jobs pack is a great way to find your next gig. It’s worth noting that the jobs pack is not accessible from every search query, but it pops up when you’re looking for specific job opportunities in certain disciplines and locations.
This pack contains different types of results: Job listings (with company names), top stories about companies hiring, education info on colleges/universities with available openings, and other relevant information that is helpful towards attaining the position you seek.
As always, make sure all your online resumes are complete so they show up in searches!
The Jobs Pack can be accessed using many different keywords related to employment queries. For example, search “jobs near me” and it will show you all the local listings that are hiring right now including salary ranges, requirements and contact information—everything you could need all in one place!
The following is an example of a Jobs Pack for the query “cashier jobs”:
Even better is knowing that these results have been verified so they don’t include scams or unqualified applicants like other sources might. And when you’re ready to make a change in your profession? A quick search will uncover opportunities from every industry across the globe.
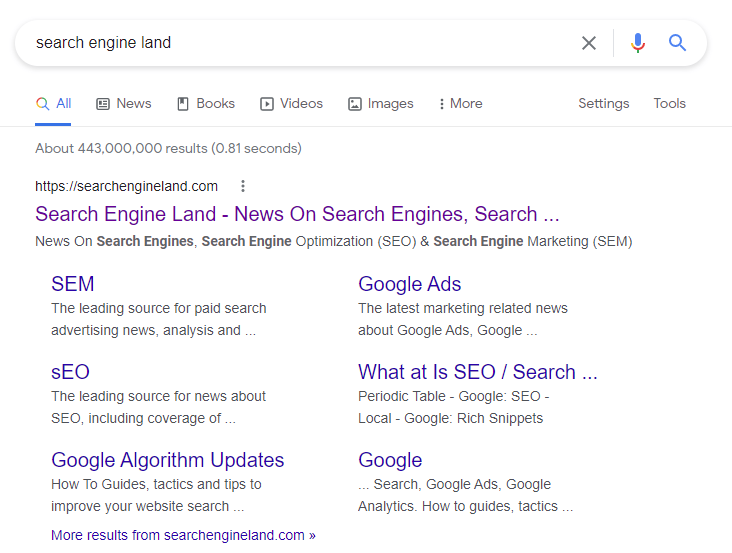
Sitelinks
Google’s Site links are another SERP feature. Sitelinks are links that may appear above the organic search results and below the advertised content. These sitelinks provide information on a website’s inner pages like contact info, hours of operation, or an event calendar without requiring users to click through from their SERP landing page.
The main benefit of Sitelinks is that they are navigational and help users get to your website easier when they are at the top of the SERPs.
Here is one example of Sitelinks, this one on Search Engine Land, when you’re looking for the brand name:
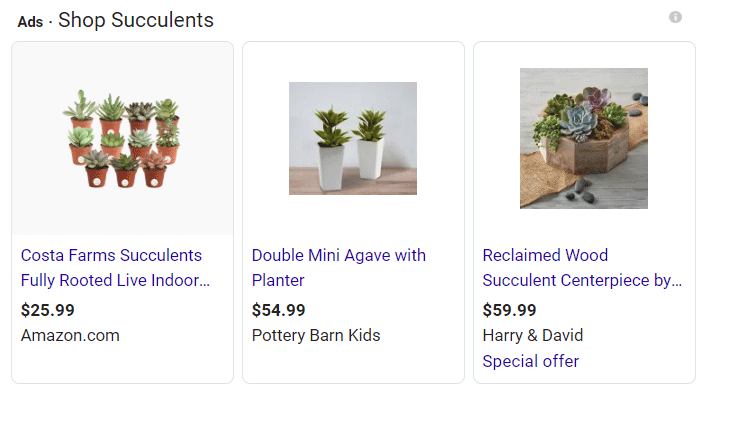
Shopping Pack
The Google Shopping Pack allows you to buy products directly on Google, giving you the option to compare prices and product reviews. Google Shopping is also available in a desktop version, so users can navigate through multiple tabs while shopping from home or work on their computer.
When searching for different products, be sure to check out this pack first! If you have difficulty locating the pack, type “shopping” into the search bar to locate it.
A shopping tab will appear at the top of your screen and scrolling down will show different products that are available for purchase on Google.
You can also click on a specific product if you want more information about size or color in order to make an informed decision before buying! These types of queries can attract a high volume of traffic and lead to an increase in rankings, so be sure not to miss out on these types of queries if you are an e-commerce website.
When you have a presence on Google Shopping, users will have the option to compare prices and product reviews for different products. Having these options is beneficial for both consumers and sellers looking to get their business noticed online!
The following is an example of the shopping pack for the query “succulents”:
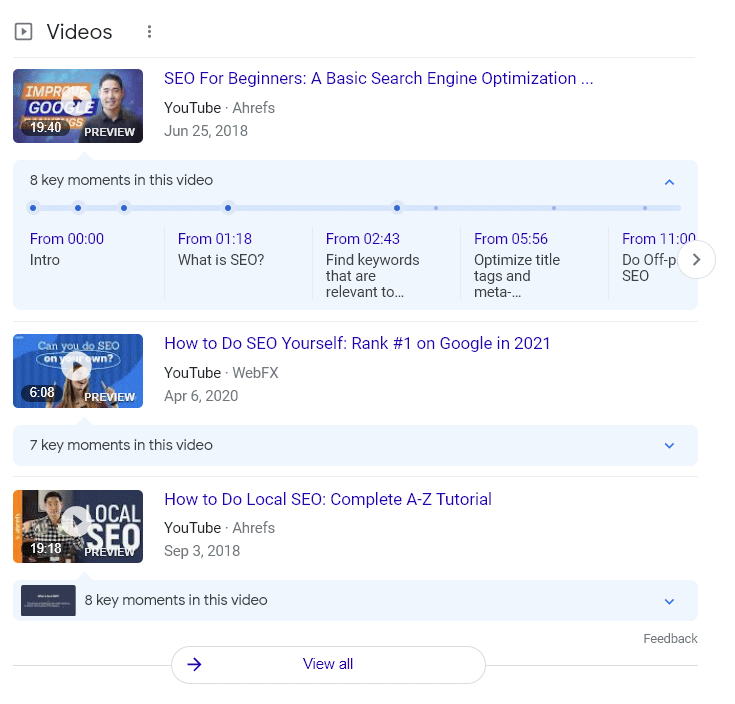
Video Carousel – Replaced with Google Key Moments
Google’s video carousel is a SERP feature that allows you to watch videos for answers. Carousels within Google’s search results are a method of finding relevant videos for your search. Users can now view video results without leaving the SERP page and still get their original query answered in text form, all with one click or less.
The video carousel has been updated with an entirely new type of video result: the new key moments video interface. After about a year of testing, they rolled it out in approximately March 2021. Barry Schwartz wrote a post about these types of results.
The following is an example of the key moment videos interface:
Google’s Search Results Offer More Opportunities to Rank and be Visible
If you’re still one of those marketers who’s only focused on the purely organic ten blue links search results, don’t be intimidated.
The more you broaden your horizons and diversify your ranking strategy, the better. You don’t want to pigeon-hole yourself by focusing on just one type of Google snippet.
Add more engagement objects to your marketing mix like videos, and earn links through amazing content.
Become well-versed in how to optimize for all of these snippets.
In doing this, you diversify your ranking strategy. If Google does an update and tweaks some snippets, you won’t have to worry about it too much.
This is where some marketers go a bit overboard— they target only one type of search result. When Google makes tweaks to a certain snippet, they decimate rankings and traffic overnight for that snippet, so rankings and traffic tank afterward.
Diversifying your strategy helps keep your SEO future-proof. How do you plan on diversifying your SEO strategy?