If it seems like your Google search results are more spot-on than ever, you likely have semantic search to thank. This type of search understands meaning and context rather than just individual words, and it’s being used to deliver the highest-quality search results yet.
Want the site you’re optimizing to benefit from semantic search? Then you need to learn how to implement semantic SEO. And if you’re a complete semantic SEO beginner, don’t worry—the tips you’ll find ahead are straightforward, easy to execute and highly effective.
What Is Semantic SEO?
To set the stage, let’s first look at the dictionary definition of semantic. According to Oxford Languages (and courtesy of Google), something that’s semantic is “relating to meaning in language or logic.”
Knowing this, the concept of semantic search is much easier to understand. In short, semantic search involves search engines finding results that relate to each query’s meaning rather than literal keyword matches.
Why is semantic search important? It all comes down to the user experience: When users enter a query that can be correctly answered in more than one way, they would rather search engines provide results that address the true meaning of their query rather than results that include the same keywords but don’t actually tell them what they need to know.
To show you what we mean, let’s take a look at Google’s BERT algorithm. Short for Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers (catchy!), BERT is a machine learning model that can “consider the full context of a word by looking at the words that come before and after it.”
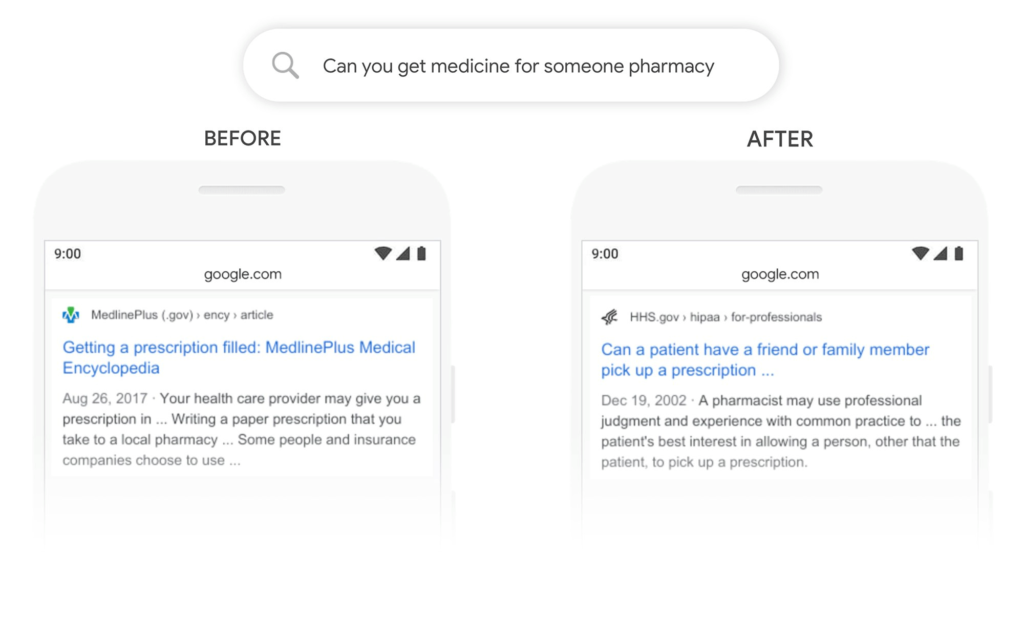
Google’s provided example illustrates this well. For the query Can you get medicine for someone pharmacy, BERT helps Google understand that the user wants to know if they can pick up a prescription for someone else, not how the prescription filling process works:
So if you’re wondering whether Google uses semantic search, BERT’s functionality alone shows that the answer is a solid yes.
And knowing what semantic search is, it’s now possible to fully grasp what semantic SEO refers to: In a nutshell, it’s a type of SEO that’s designed to cater to search engines’ efforts to address the semantic meaning behind users’ queries.
How Has Semantic Search Changed SEO?
As you might imagine, the emergence and advancement of semantic search had a profound impact on SEO as a whole.
After all, before search engines were able to accurately understand the meaning behind users’ queries, all a webmaster had to do to boost their rankings was include the right keywords and do some link building (that’s why keyword stuffing and link schemes ran so rampant in the early days of the internet).
But after search engine algorithms started becoming more semantically intelligent, it became harder and harder to game the system. The standards of content quality rose exponentially, and SEO practitioners had to build increasingly sophisticated skill sets.
Those things remain true today, and with the June 2021 release of Google’s page experience update it’s clearer than ever before that a great page is worth more than the sum of its keywords.
With semantic search being as important as it is, SEO pros now have to account for more nuanced concepts than keywords and links. These can include (but certainly aren’t limited to):
- mobile-friendliness;
- anchor text SEO;
- schema markup;
- user intent; and
- expertise, authoritativeness and trust (E-A-T).
And in order to optimize for semantic search specifically, SEO practitioners need to adopt semantic SEO practices. When implemented properly, these practices can not only improve your visitors’ experience but also boost search rankings.
How to Leverage Semantic SEO for Your Site
Now you know what semantic SEO is and why it’s important, but how can you incorporate it into your real-world SEO efforts?
If you’re a beginner, you’ll be glad to know that semantic SEO practices are both intuitive and easy to grasp—if you can understand that gummy bears fall under the topic of candy but the Eiffel Tower does not, then you can practice semantic SEO.
Follow these beginner-friendly semantic SEO tips to bring your SEO strategy to life.
Stay On-Topic
Semantic SEO often comes down to topical relevance, or the extent to which a website (or individual page) covers a certain topic.
For instance, a page that covers 15 different unrelated topics could be perceived as spammy or un-authoritative, while a page that covers one topic thoroughly is more likely to be perceived as high-quality (this is doubly true when the page’s parent website has authority on the same topic).
So if you want to ensure your content is topically relevant and authoritative, always:
- keep each page on-topic, and don’t stray too far from the purpose of the overall website;
- cover each page’s topic as thoroughly as possible;
- cite your sources; and
- only link out to trustworthy sites.
Use Semantic Keywords
When performing keyword research, it’s tempting to simply find a primary keyword, come up with a couple variations of it and call it a day.
But if you’re practicing semantic SEO, you need to go one step further by incorporating semantic keywords too. What are semantic keywords? They’re simply words or phrases that are related to each other by concept. Put differently, they don’t need to share the same words, just the same topic.
For example, let’s start with the primary keyword pyramids. Semantically related keywords could include:
- Ancient Egypt;
- Great Pyramid of Giza; and
- ancient architecture.
Similarly, let’s start with the keyword healthy dinner recipes. Semantically related keywords might include:
- what is a good dinner for weight loss;
- keto diet; and
- low-carb meals.
So when you’re building your content creation strategies or writing a new piece of content, remember to include semantic keywords in order to capture the most traffic possible.
Answer Users’ Questions
Since semantic search places such a large emphasis on understanding what users are looking for, you can increase your chances of ranking higher by answering as many relevant user questions as possible.
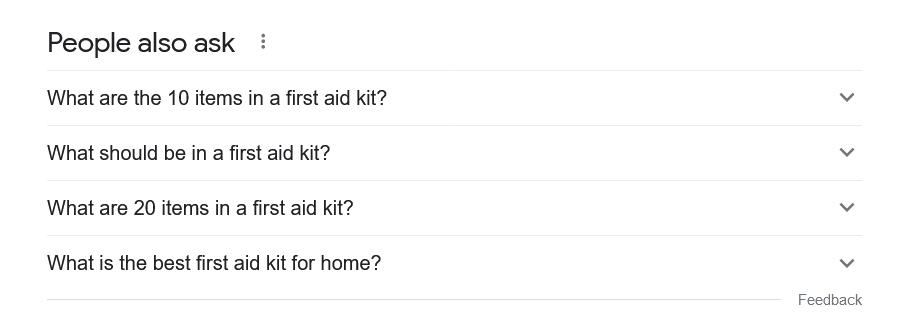
To see the kinds of searches real people are making about a given topic, one of the best resources is Google’s own People also ask (PAA) box. This box shows up on the first page of search results and will initially display about four questions.
For instance, here is the PAA box for the query first aid kit:
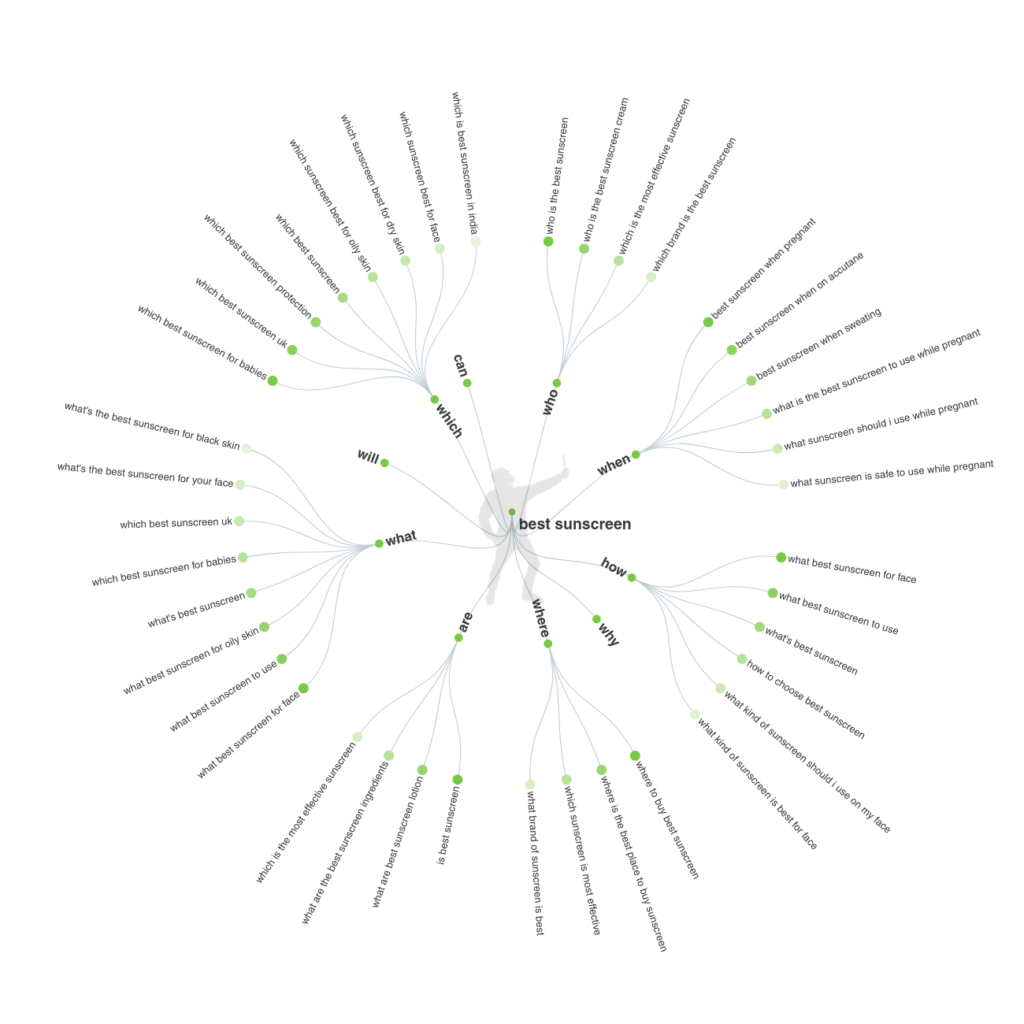
Another option is to use a tool like AnswerThePublic. To use it, simply enter a keyword or phrase and you’ll be shown a robust collection of questions people pose to search engines about it.
In this example, we’ve entered the key phrase best sunscreen. The results include queries like “what sunscreen is safe to use while pregnant,” “what’s the best sunscreen for your face” and “which is the most effective sunscreen:”
These results can serve as an ideal jumping off point for creating in-depth content that addresses the true meaning behind users’ searches.
Implement Structured Data
While structured data isn’t strictly necessary for telling Google what your site’s content is about, it does make it easier for Google to understand and categorize your content in a timely manner.
So if you use structured data, then you’ll have a better chance of ranking higher for the most semantically relevant topics. And while various structured data formats such as JSON-LD exist, Microdata is the most widely used.
If you’re not already familiar with Schema, it’s summed up best on the format’s official community site:
When used on a site, Schema markup serves to organize content by both hierarchy and type. On a page that’s classified as an event, for instance, various properties can tell search engines:
- who the intended audience is;
- when the event will take place;
- where the event will be held;
- the person or organization funding the event;
- the person or organization hosting the event;
- the maximum number of attendees; and
- the typical age range of attendees.
So if a user makes a query for harvest festival family friendly and the festival’s page utilizes Schema markup, Google will be able to understand the semantic meaning behind the query and successfully extract the correct information (in this case, the typical age range of attendees) from the page.
Add Image Alt Text
Google may have highly advanced visual recognition AI models, but that doesn’t mean it couldn’t use some help deciphering the contents of your site’s images. After all, there are billions upon billions of images on the web and Google can’t apply its most sophisticated AI to every single one.
To help Google understand what your site’s images depict, you can simply take a couple minutes to add image alt text to each one.
Consisting of only a sentence or two, that alt text will describe each image in a way that Google’s crawlers can quickly and easily understand (no crawl budget issues here!). Plus, alt text will also help improve your site’s accessibility for visitors who are blind or have visual impairments.
But most importantly for the purposes of this article, image alt text will boost your site’s semantic SEO when users are searching via Google Images rather than performing a standard Google Search.
Here’s how it works: When you add alt text, a description of your image is hidden within the page’s HTML code. In other words, search engines will be able to see it but visitors will not.
To see alt text in action, we can right click on of the images from our own anchor text SEO article and click inspect to view its source code. Then, you’ll be able to see the alt text exactly as it was originally written:
Alt text isn’t hard to implement, but it can make a big difference in terms of semantic SEO, site crawlability and accessibility alike.
Deliver Value
At the end of the day, it’s crucial to remember that the entire purpose of semantic search is to give users better search results than before. So even if your pages are on-topic and loaded with all the right keywords, alt text and Schema markup, you’re unlikely to achieve the SERP rankings you’re after if you fail to deliver true value to visitors.
So in your pursuit of top-notch semantic SEO, don’t lose sight of the ultimate goal: creating pages that tell visitors exactly what they want to know, thoroughly answer their most burning questions and maintain a high standard of quality.
Beginner-Friendly Tactics, Advanced Results
If you don’t think semantic SEO seems all that difficult, then you’re absolutely right. Since semantic search is all about understanding what real humans want when performing a search, anyone who’s human can optimize for it.
So unless you’re an alien, you don’t need to learn a whole new skill set in order to master semantic SEO. Just follow the easy tips in this guide and you’ll be well on your way to higher rankings, more visitors and better content.
Image credits
Google / October 2019
Screenshots by author / June 2021
AnswerThePublic / June 2021