Do you want to get better results from your SEO efforts? If so, one of the first steps you can take is to look at how effective your pages’ title tags are. This could result in a significant increase in traffic in as little as ten minutes, depending on your niche.
Page titles, or title tags, are a fundamental part of on-page SEO. Just by making simple changes to your title tags, you can generate significant improvements in your SERP performance.
If you are looking to improve the impact of your website’s SEO, this is an important first step.
Table of Contents
SEO 101: What Is a Title Tag?
What is the Syntax for the Title Tag?
Why the Title Tag is Important
Title Tags – Where Do They Show Up?
How to Write Title Tags That Increase Click-Through Rates
Every Page Must Have a Specified Title Tag
Title Tags Must Be Descriptive and Concise
Title Tags: Don’t Stuff Your Titles With Keywords
Separators in the Title Tag
Title Tags: Common SEO Mistakes
Over-Optimization
Missing Titles
Under-Optimization
Duplication of Titles
Titles Are Too Short
Titles Are Too Long
SEO 101: What Is a Title Tag?
Not familiar with HTML elements? Not a problem: a title tag is simply a clickable bit of text at the top of your search snippet in the search results. This precedes the meta description part of your listing. In a page’s code, the title tag is represented by <title>.
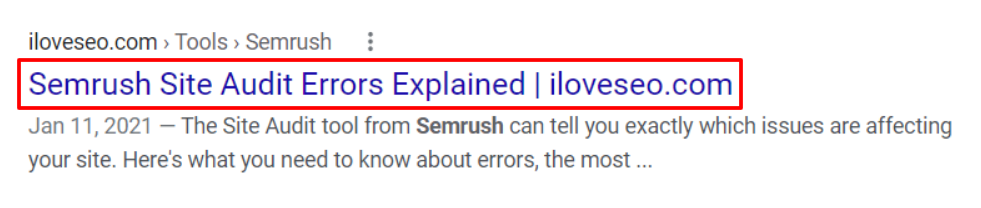
Take for example the SERP listing for one of our own articles:
There are different beliefs when it comes to creating title tags. While some believe that 70 characters is the sweet spot, others believe that 110 characters (on mobile) is when the cut-off occurs. Either way, there is no magic number that you have to hit in order to optimize your title tag perfectly.
This tag shows up in both the tab of your browser window, and it shows in pages’ code too.
What Is the Syntax for the Title Tag?
The following is the syntax of how this tag appears:
<title>This is an example page title | Brandname</title>
Modern websites use a CMS, or content management system, to manage their website along with its content. One of the most common in use today is WordPress. In WordPress, you can usually fill out a form field that helps you fill in the title tag, and the CMS also generates all the code for you so there’s no heavy lifting required on your part.
For you, the hard work will lie in competition analysis and assessing how you must write your title tag in order to be successful.
It’s also important to note here that title tags are also referred to as page titles, HTML titles and meta titles alike. It all depends on who you talk to and the specific name they prefer.
Why the Title Tag Is Important
When a user stumbles across your title tag in the SERPs, this is in many instances the first piece of information they have to judge which search result to actually click on.
For this reason, Google recommends using high-quality titles that are descriptive, concise and unique.
Title Tags: Where Do They Show Up?
They show up in three places:
In the search results above your meta description,
On other websites,
In the browser window.
In the Search Results
The page title tag shows up in the Google search results prominently. Changing the title tag to something more effective than what you have right now could have a potentially big positive impact on your click-through rates.
As you can see above, the page title tag shows up in the search results above the meta description tag.
On Other Websites
It is not unheard-of for other websites to link back to a page using its title tag in the all-important anchor text. When you have an engaging and well-written page title tag, you have an opportunity to rope in visitors from other websites as well.
This other dimension must also be considered when writing your title tags.
How to Write Title Tags That Increase Click-Through Rates
As touched on above, Google has specific recommendations for how to write title tags that have a positive impact on click-through rates.
Per their guidelines, make sure your title tags are:
- included for every page on your site;
- descriptive and concise;
- free of keyword stuffing;
- completely unique (no boilerplate content allowed); and
- succinctly branded.
Let’s take a closer look at some of those tips.
Every Page Must Have a Specified Title Tag
One of the first of Google’s instructions is that there must be a specified title tag on the page itself. From this, we can infer that every page you want Google to index should have its own title tag.
Here’s why: there are many sites out there with hundreds or even thousands of pages. Logistically speaking, it would be impossible to create page titles for so many pages in a realistic time frame (unless you happen to be an extraordinarily fast typist, of course).
So, the reasonable solution is to create page titles only for pages you want to show up in the SERPs.
Title Tags Must Be Descriptive and Concise
It is imperative that you write descriptive but concise page titles. Some may not believe this, but Google also advises against using a title like “Home” for your home page, or “Profile” for someone’s profile page:
If your page is about real estate in Chicago, then you may want to instead write your home page title as the following:
Real Estate in Chicago | RealEstate Company, Inc.
But if your page discusses real estate financing and is all about mortgages and qualifying for a mortgage, you may write it in this fashion instead:
How to Qualify for a Real Estate Mortgage | RealEstate Company, Inc.
Figure out exactly what page title will describe your page while also remaining concise and integrating your keywords naturally.
Don’t Stuff Your Titles With Keywords
Google recommends not stuffing your titles over and over again with different keywords. All this does is it creates confusion regarding what your page is really about.
In the past, less-than-reputable SEO practitioners would add keywords (sometimes more than three times) in the page title repeatedly. This was done to manipulate the Google search results into rewarding their pages with higher rankings.
This practice also serves to hurt the user experience, though. Not everything that’s good for the user experience is good for SEO, however.
Google says that doing keyword stuffing nowadays can also hurt your site’s search rankings.
Don’t Use Repeated or Boilerplate Titles
Google’s recommendation, in short, is to entirely avoid using repeated or boilerplate titles. Again, they reiterate that distinct, descriptive page titles are very important.
Making every title on a site the same does not make it easy for consumers to differentiate one page from another.
This doesn’t mean that you can create long titles where just one minor piece of information is different, either. The uniqueness of the page title when it comes to describing the page is of paramount importance.
For larger sites, Google does recommend dynamically updating the duplicate page titles to better include information that accurately describes the content of the page.
Their example goes further, saying that you should only include things that reflect the content of the page.
They also say that you can even use the organization name as a concise title while piggybacking on the meta description to describe your site’s content.
Next time you are asked if writing unique page titles is really a good use of your team’s time and resources, simply point to Google’s own guidelines.
A Quick Note about Google Rewriting Title Tags
Let’s say you’ve just written your most accurate page titles yet. You spent hours on just a single title, and you reviewed your chosen optimization strategies again and again.
But, despite all that, Google could still decide to rewrite your carefully crafted page title.
This issue has been a thorn in the side of SEO practitioners for a long time. In fact, it’s happened so often that some SEO professionals have wondered if it’s even worth it writing custom title tags anymore. Google’s advice, though, is to simply make your page titles as relevant as possible and let its algorithm do the rest:
“If we’ve detected that a particular result has one of the above issues with its title, we may try to generate an improved title from anchors, on-page text, or other sources. However, sometimes even pages with well-formulated, concise, descriptive titles will end up with different titles in our search results to better indicate their relevance to the query. There’s a simple reason for this: the title tag as specified by a website owner is limited to being static, fixed regardless of the query.
When we know the user’s query, we can often find alternative text from a page that better explains why that result is relevant. Using this alternative text as a title helps the user, and it also can help your site. Users are scanning for their query terms or other signs of relevance in the results, and a title that is tailored for the query can increase the chances that they will click through.
If you’re seeing your pages appear in the search results with modified titles, check whether your titles have one of the problems described above. If not, consider whether the alternate title is a better fit for the query.”
That’s it in a nutshell. Google also notes that if you feel that you are following everything in the guidelines as noted above but are still encountering problems, then you may want to let them know in their Search Central help forums.
Title Tags: What Is the Best Length?
First, it’s helpful to examine some of the popular misconceptions about title tags. There are many opinions on what is the best length for a title tag. Depending on the source you turn to, you may be told the title tag:
- must be approximately 60-65 characters long;
- must be less than 70 characters long on mobile devices;
- can be up to 110 characters long on mobile devices; or
- must be 56-60 characters long,
All of these recommendations are based on ensuring that all keywords, phrases and applicable information appear before the cut-off point.
In this case, Google Search Central does not mention anything about the maximum number of characters you should observe.
Moz, however, says the optimal title length is approximately 50-60 characters. Their reasoning is that this helps ensure your title tags continue to display properly and Google doesn’t have to rewrite or truncate them.
Separators in Title Tags
When creating title tags, one element that many SEOs focus on is the separator, sometimes too much. Google has said that they treat this separator the same whether it’s a dash (-), a vertical bar (|) or a colon (:).
These are simply the main ones that most SEOs use. There are, however, many different types of separators that you may use. You can use arrows, underscores, greater-than and less-than symbols, emojis and a myriad of other types of separators!
The list is nearly endless. Here is just a sample:
- Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet + Name of Your Blog
- Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet * Name of your Blog
- Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet ~ Name of your Blog
- Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet < Name of your Blog
- Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet > Name of your Blog
- Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet _ Name of your Blog
- Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet @ Name of your Blog
This is not every single separator available, though. You may want to experiment with them and see exactly which ones work best with your site.
Title Tags: Common SEO Mistakes
Believe it or not, many SEO pros (and non-SEO pros) make serious mistakes with their title tags. From over-optimization to under-optimization to missing tags, some of the mistakes range from silly to serious.
Be that as it may, let’s examine some of the more common SEO mistakes to make sure that you’re not shooting yourself in the foot with your SEO.
SEO Mistake 1: Over-Optimization of Title Tags
Over-optimization is easy to spot. Ideally, most title tags allow you to optimize one keyword per title tag based on characteristics like the title tag’s length, its optimization compared to competitors and other factors.
The first mistake you will be able to identify includes over-optimization. This includes using the primary keyword more than twice, which is never a good thing in Google’s eyes.
It won’t necessarily lead to a penalty, but it could lead to an algorithmic devaluation if done excessively.
SEO Mistake 2: Missing Title Tags
Missing title tags are never ideal. Title tags, by their definition, establish the theme of the page along with the h1 heading tags. In other words, they serve to tell Google what your page is about.
So if you are missing title tags, you are missing critical information that Google needs to know about your page.
This mistake happens more often than you may think. The recommendation here is always to make sure that your title tags are present and include relevant information to help Google (and users) understand your page.
SEO Mistake 3: Under-Optimization of Title Tags
Under-optimization of title tags is also possible and can result in not being competitive enough to rank. This is just as (if not more) dangerous as over-optimization.
When your title tags are under-optimized, you leave your site open to not ranking at all. And, worse still, you also leave your site open to underperformance.
This is why it’s important to understand the specifics in your niche and how things vary between SERPs. Significant ranking improvements can come down to just a single title tag and updating it to better reflect user intent and accurately match the page’s content.
SEO Mistake 4: Duplicate Title Tags
Duplicate title tags are also bad news, because when you have many pages titles that are exactly the same then you introduce confusion to users and search engines alike.
And when you introduce such confusion, you may end up taking a ranking hit as a result, because Google cannot accurately understand the meaning behind your title tags.
This is true even if only a portion of your titles are duplicated. For example, if the first part of your title tag is always the same, but the second part is different for every page, that still doesn’t mean it’s a unique title tag. If, however, you include the brand name in this scenario rather than specific information, you don’t have to worry about duplication.
SEO Mistake 5: Title Tags That Are Too Short
It’s possible to have title tags that are too short. In general, this occurs when they are less than approximately 30 characters.
You are most likely not able to convey the meaning and content of the page enough in 30 characters.
SEO Mistake 6: Title Tags Are Too Long
Having title tags that are too long is another common SEO mistake. In most SEO circles, this is defined as being longer than 56-60 characters.
The idea behind this mistake is to make sure that your title tag is not cut off by an ellipses (…) in the search results.
Most SEO practitioners believe that a title that’s cut off by an ellipses is a bad thing. However, this is not always the case. For instance, it may be that your competitors are writing slightly longer and different title tags than the norm because someone found out that this is what Google is rewarding.
From a user perspective, having important information about the page cut off by the ellipses is less than ideal. However, Google can still see this information. Google Webmaster Trends Analyst Gary Illyes is on record as saying that there is still some SEO benefit to having information behind the ellipses.
So, just make sure that all the important information users need is included before the ellipses and you’ll be good to go.
Writing Title Tags is Half the Battle
The other half includes seeing results from your SEO strategy. Don’t forget to always be testing.
If you continue testing title tag changes, you may find that certain variations will bring improvement to your rankings, traffic, and overall conversions.
Unless you are already intimately familiar with your industry and you know what works, ongoing testing should be a part of your overall SEO strategy.
Image Credits:
Screenshots by author / March 2021
Screenshot of Google Webmaster Guidelines by author / March 2021