For those who are not aware, keyword research involves performing research for keywords for your site that you can then create content for. But in recent years there has been a bit of a shift from keyword optimization and targeting to entity optimization and content topic research.
Should You Ignore Keywords and More Standard Methods of Keyword Research?
While topic and entity research are gaining popularity, you should absolutely not ignore more traditional keyword research tactics. They should still be a major part of your strategy, and they lay a strong foundation for finding keywords you may not have otherwise thought about.
So, the pragmatic thing to do is continue performing thorough keyword research while also linking and optimizing for entity-related keywords and phrases.
To do so effectively, think of your site as an entity database that supports a particular topic. This is how your entire optimization strategy will be born.
Ideally, your main topic should be covered on-site, with supporting pages for that main topic throughout which serve to cover it as comprehensively as possible.
This is how entity SEO becomes so powerful: with topic reinforcement and getting so in-depth with your topic content that you blow competitors out of the water.
What Is an Entity, Anyway?
According to a patent filed by Google, an entity is “a thing or concept that is singular, unique, well-defined and distinguishable.” It goes on to say that an entity can be a:
- person;
- place;
- item;
- idea;
- abstract concept;
- concrete element;
- other suitable thing; or
- any combination thereof.
Notice that list doesn’t include specific words or phrases; Instead, it only includes the actual entities that words or phrases may be referring to.
Translation? The days of exclusively targeting specific keywords and phrases are over, and the days of topic targeting, topic research, topical focus reinforcement and entity optimization are the future of SEO.
So, topic and entity research, optimization and targeting should all be a part of your overarching strategy.
Let’s take a look at all three and how they play into the larger picture of modern SEO.
Initial Topic and Entity Research
Using Google Search, we can move forward with preliminary topic research and nail down topics and entities that will benefit your site in the SERPs.
If you have never performed entity research before, you may be glad to hear that it’s largely the same as keyword research. The only difference is that in place of keywords, you are using entities.
When shifting from keyword research to entity and topic research, ask yourself the following questions:
- What does Google know about my site?
- Which topics and entities does Google associate with my site?
- How can I write content to optimize for those topics and entities?
- Which topics should I be writing about?
When you want to find out what Google knows about your site and discover how it sees it for your particular topics and keywords, you can take one of our favorite Google search tips and use the following operator syntax:
site:example.com [topic]
It’s important to note that this is not accurate all of the time, but it is accurate enough times that you can use it to spot problems.
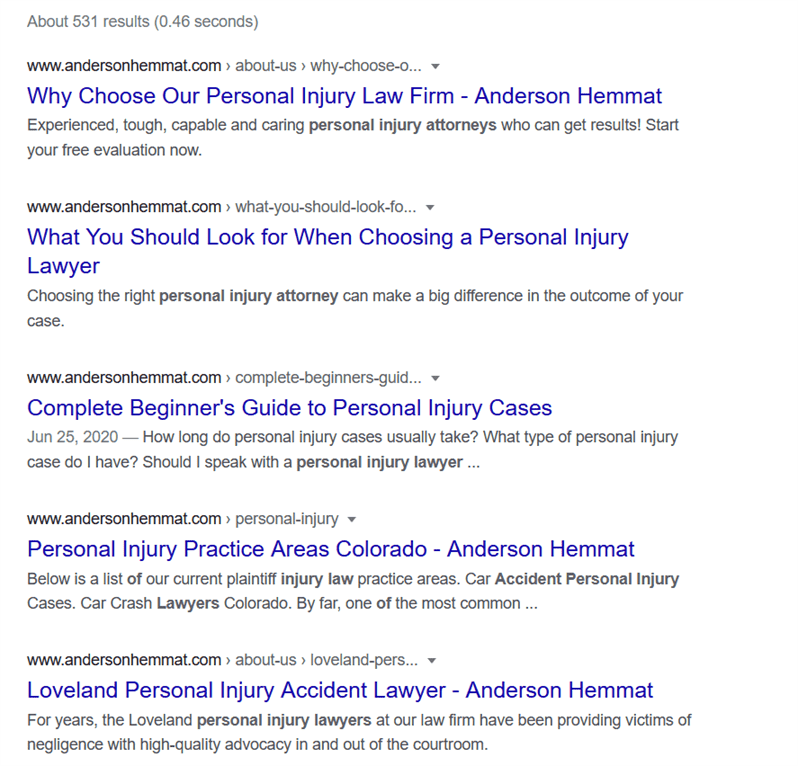
Going back to the Denver attorney website competitors we used in our chapter on competitor research with Semrush, let’s take a look at how Google sees them. For this example, we’ll examine the Anderson Hemmat, LLC law firm using the query:
site:andersonhemmat.com personal injury lawyers
The resulting SERP will only display listings for the specified website that also include the specified topic:
In this particular SERP, several of the website’s pages show up. The first page of results includes the law firm’s:
- about us > why choose our personal injury law firm page;
- what you should look for when choosing a personal injury lawyer page;
- complete beginner’s guide to personal injury cases page;
- personal injury practice areas page; and
- location-specific about us subpage.
Notice how the first result is not the firm’s homepage. In fact, the homepage doesn’t show up anywhere in the top five results. That’s because the firm has optimized its site for topics that people actually search for (such as what to look for when choosing a personal injury lawyer) rather than keywords alone.
In other words, Google doesn’t just associate the site with the personal injury lawyers key phrase—it also associates it with the personal injury lawyers entity, and therefore displays a wide range of results that are intuitively organized by topic.
Imagine the competitive edge that you could have if you also differentiated your site structure and content to support your main topic and provide the solutions people search for. It’s certainly worth a shot.
In-Depth Topic and Entity Targeting and Optimization
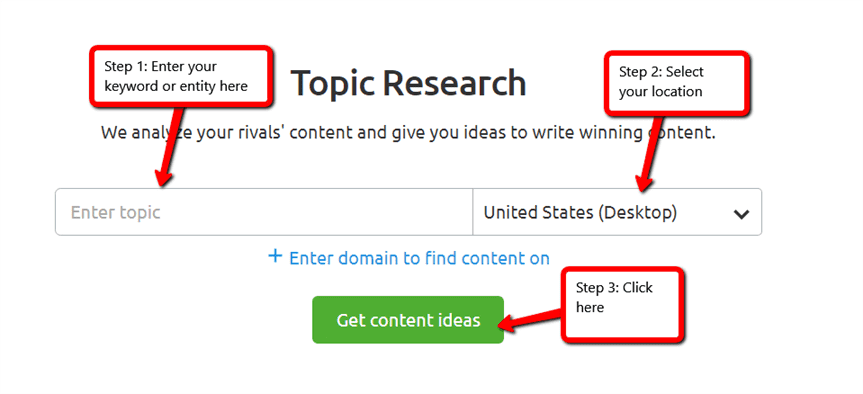
Using Semrush’s Topic Research tool, it is possible to plug in topics and entities to figure out exactly which ones will help you perform better in the SERPs:
The basic steps, as shown in the graphic above, are:
- Enter your keyword or entity.
- Select your location (including your target region and/or city, if desired).
- Click the green get content ideas button.
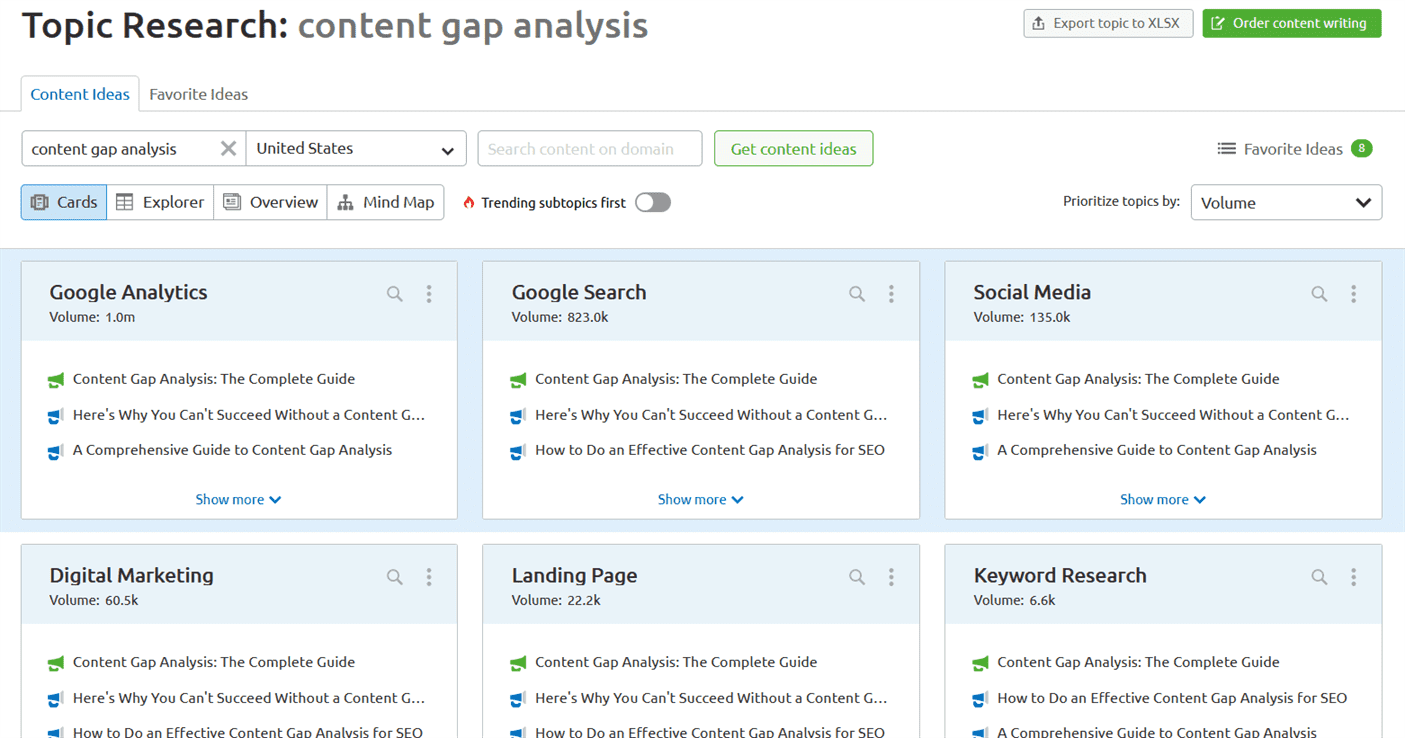
A screen resembling the following will load. For our purposes, and the example, we are using the topic content gap analysis:
Here, you have different options that you can use to see how these ideas intersect and impact one another. For instance, you can view the ideas in the form of cards, or you can visualize them as a mind map.
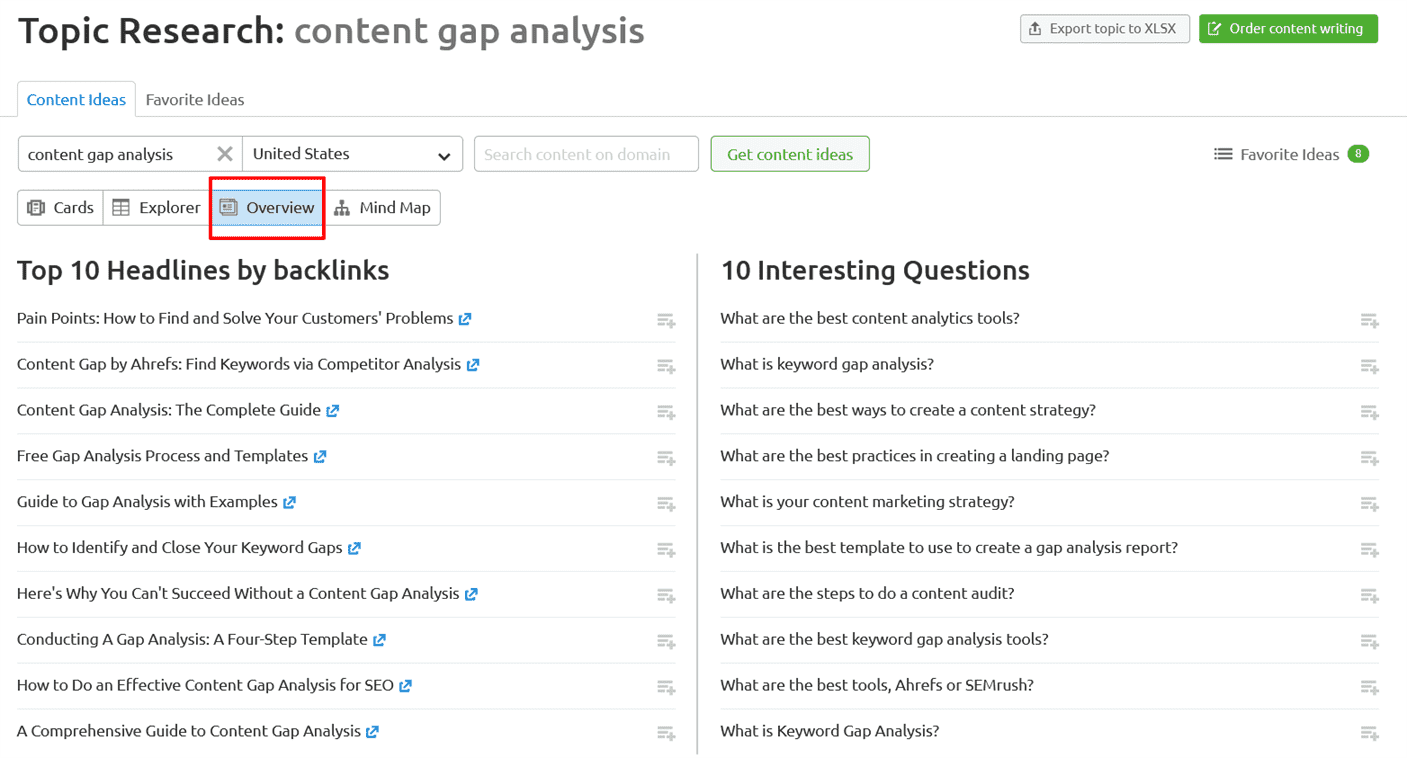
This tool is a fantastic way to get a bird’s-eye view of your topic in your niche and see what’s already being written about. The information it provides will give you an idea of what you’re up against in terms of the competition for that topic.
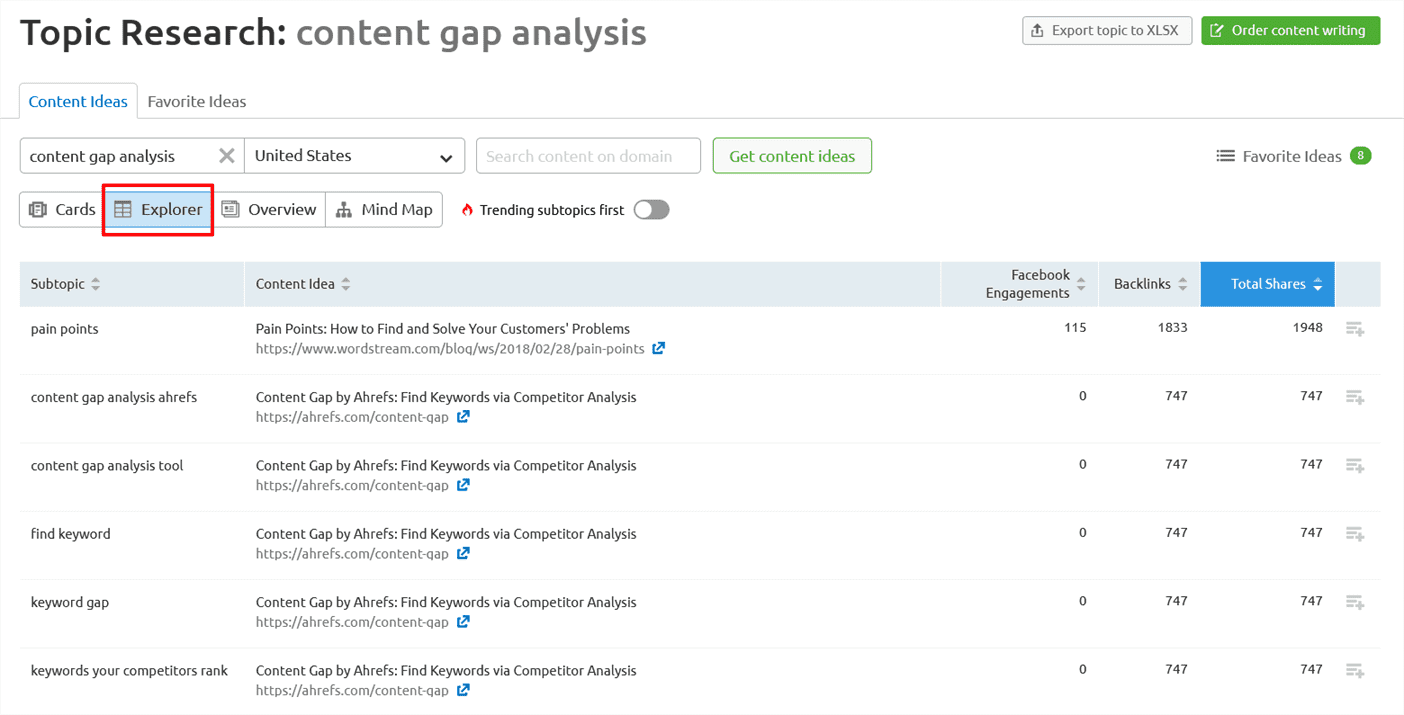
It also provides different options you can use to see how these ideas intersect and impact one another. If you click on the explorer button, for example, you will be able to see what kind of Facebook engagement each subtopic has, top pages for the topic, the amount of backlinks to those pages and total overall social shares:
The overview section shows the top ten headlines by backlinks, ten interesting questions that people ask about the topic, top subtopics and top ten related searches:
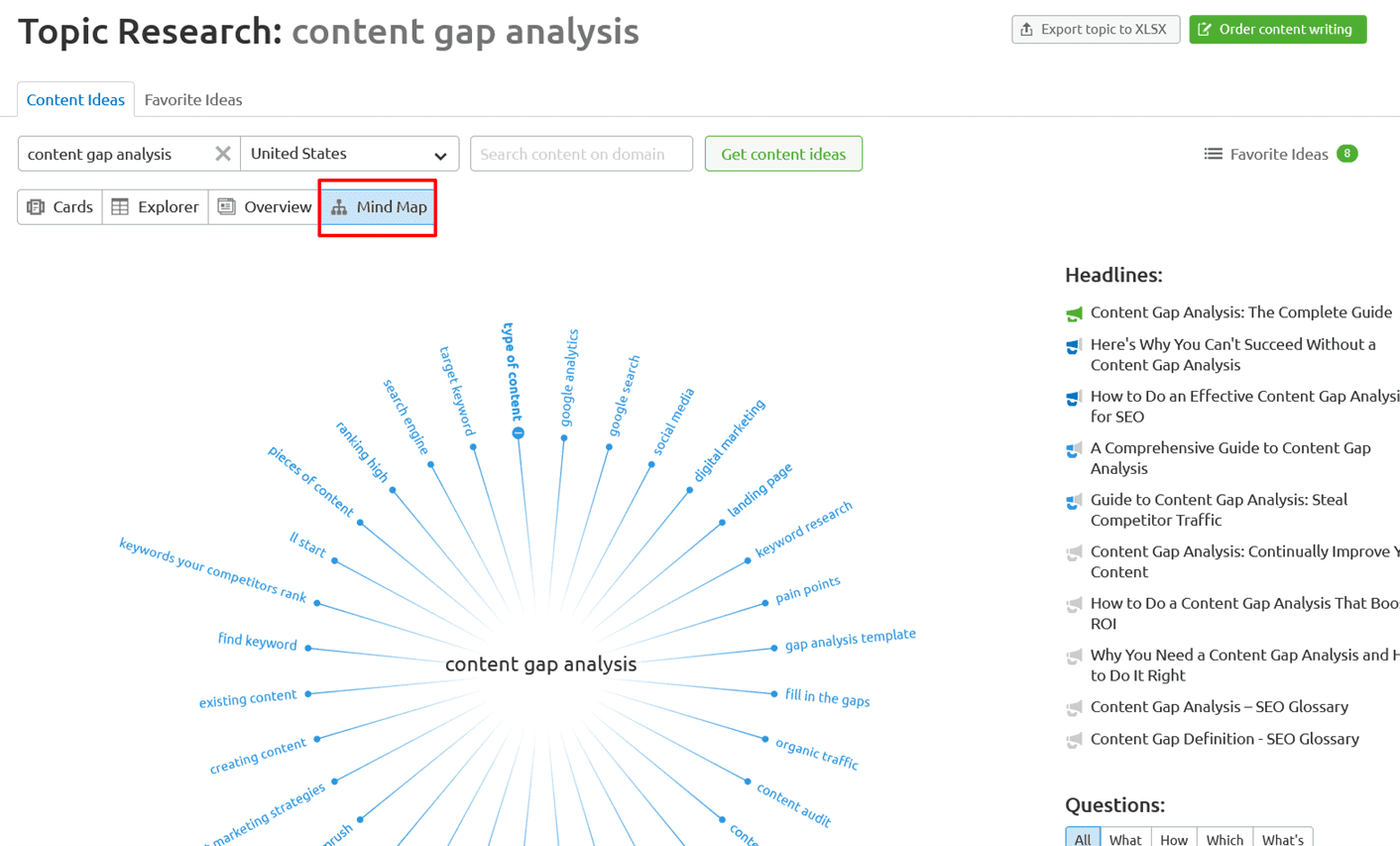
Finally, the mind map section has a content cluster diagram that will help you see how all of these different subtopics and related topics align with your main topic. It is invaluable for creating a content silo that reinforces topical focus while closing the content gap between you and your competition:
As you figure out what type of content you want to write, and which subtopics you want to put in your articles about your main topic, you will likely identify gaps in your on-site content that you will want to cover.
This is how your content strategy is born, and how it will help you in your quest to achieve SERP dominance over your competition.
After completing your in-depth topic and entity research, compile the top content ideas that you want to write about, along with pertinent questions, headlines and other data, in one central document. This will help you write on-point and on-topic articles, and ensure that they are thorough and competitive enough to rank.
The Future of Editorial Tasks and SEO
In simpler times, SEO-optimized content creation was about creating as much content with as many keywords as possible. Now, though, Google’s incredibly advanced search algorithm and rapidly advancing artificial intelligence (AI was the star of the show at Search On 2020) requires a more nuanced approach.
Luckily, Semrush’s editorial capabilities make it a snap to come up with relevant topic ideas and optimize for the entities that matter most to your site. With the Topic Research tool at your disposal, you’ll be ready for the future of SEO-friendly editorial tasks.
Image credits
Screenshots by iloveseo.com / December 2020
Screenshot by author / January 2020